ESP8266确定电机最小启动PWM的完整指南
确定电机的最小启动PWM值是实现精确低速控制的关键。以下是多种方法的详细实现。
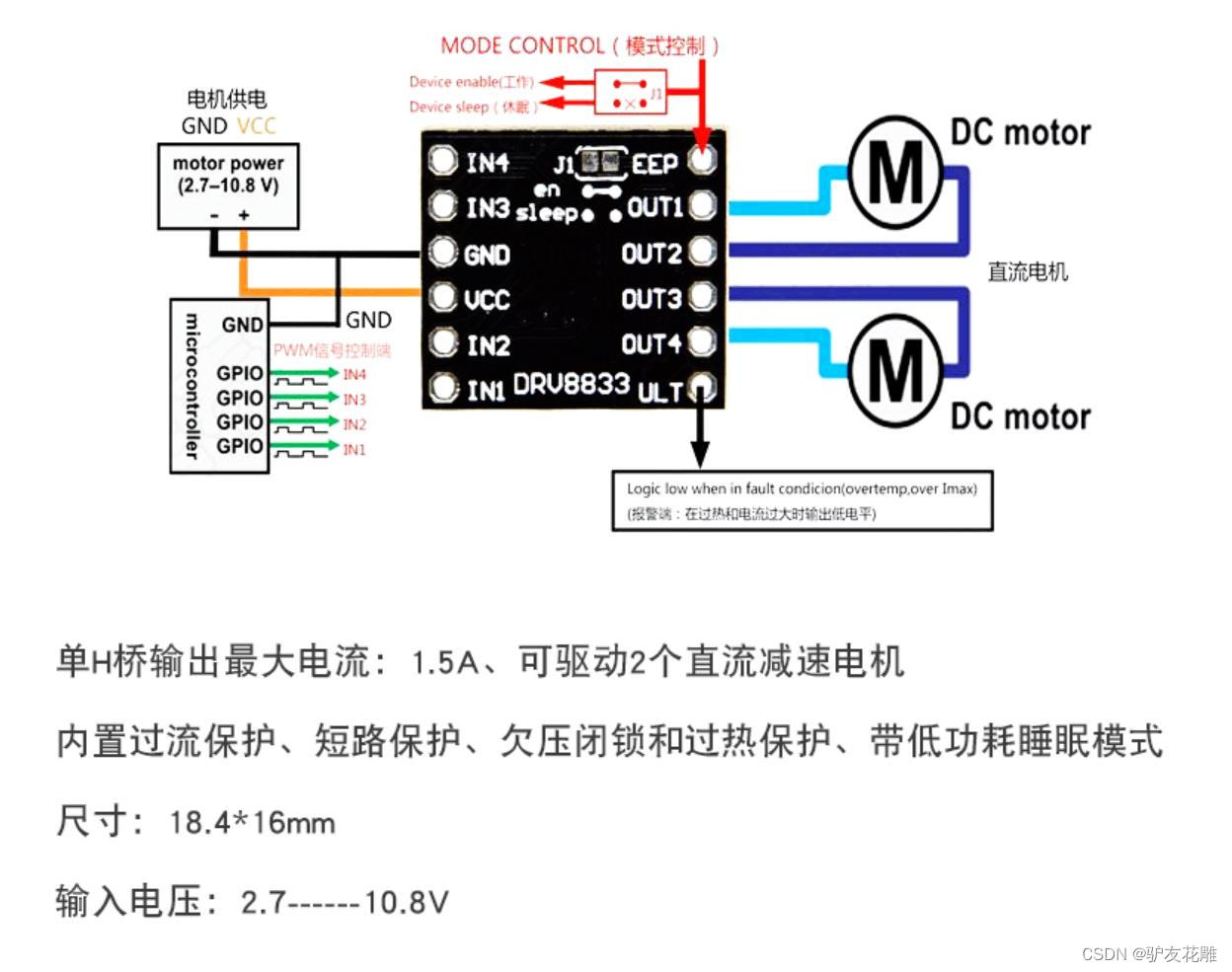
🔧 基础手动校准方法
1. 串口交互式校准
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
#include <Arduino.h>
#define MOTOR_PWM_PIN D1
#define MOTOR_DIR_PIN D2
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
pinMode(MOTOR_PWM_PIN, OUTPUT);
pinMode(MOTOR_DIR_PIN, OUTPUT);
analogWriteRange(1023);
analogWriteFreq(1000);
Serial.println("=== 电机最小启动PWM校准程序 ===");
Serial.println("指令:");
Serial.println("s - 开始校准");
Serial.println("+ - 增加PWM值");
Serial.println("- - 减少PWM值");
Serial.println("y - 确认当前PWM为最小启动值");
Serial.println("0 - 停止电机");
}
int currentPwm = 0;
bool calibrating = false;
void loop() {
if (Serial.available()) {
char command = Serial.read();
switch (command) {
case 's': // 开始校准
calibrating = true;
currentPwm = 0;
analogWrite(MOTOR_PWM_PIN, currentPwm);
digitalWrite(MOTOR_DIR_PIN, HIGH);
Serial.println("开始校准 - 从PWM=0开始");
break;
case '+': // 增加PWM
if (calibrating) {
currentPwm += 5;
currentPwm = constrain(currentPwm, 0, 1023);
analogWrite(MOTOR_PWM_PIN, currentPwm);
Serial.printf("PWM增加到: %d\n", currentPwm);
}
break;
case '-': // 减少PWM
if (calibrating) {
currentPwm -= 5;
currentPwm = constrain(currentPwm, 0, 1023);
analogWrite(MOTOR_PWM_PIN, currentPwm);
Serial.printf("PWM减少到: %d\n", currentPwm);
}
break;
case 'y': // 确认找到最小值
if (calibrating) {
calibrating = false;
analogWrite(MOTOR_PWM_PIN, 0);
Serial.printf("✅ 最小启动PWM确定为: %d\n", currentPwm);
Serial.println("请记录此值用于电机控制");
}
break;
case '0': // 停止电机
calibrating = false;
analogWrite(MOTOR_PWM_PIN, 0);
Serial.println("电机已停止");
break;
}
}
}
2. 自动步进扫描法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
/**
* 自动扫描寻找最小启动PWM
* 以固定步长增加PWM,在每个值停留一段时间
*/
void autoScanMinPwm() {
Serial.println("开始自动扫描最小启动PWM...");
Serial.println("观察电机并在开始转动时记录PWM值");
int startPwm = 0;
int endPwm = 200;
int step = 5;
int dwellTime = 3000; // 每个PWM值的停留时间(ms)
for (int pwm = startPwm; pwm <= endPwm; pwm += step) {
analogWrite(MOTOR_PWM_PIN, pwm);
digitalWrite(MOTOR_DIR_PIN, HIGH);
Serial.printf("测试 PWM: %3d - ", pwm);
Serial.println("观察电机是否开始持续转动");
// 在每个PWM值停留,让用户观察
unsigned long startTime = millis();
while (millis() - startTime < dwellTime) {
// 可以在这里添加紧急停止检查
if (Serial.available()) {
char cmd = Serial.read();
if (cmd == 's') {
analogWrite(MOTOR_PWM_PIN, 0);
Serial.println("扫描被用户中断");
return;
}
}
delay(100);
}
}
analogWrite(MOTOR_PWM_PIN, 0);
Serial.println("自动扫描完成");
}
📊 高级自动检测方法
3. 基于电流检测的自动识别
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
/**
* 基于电流变化自动检测最小启动PWM
* 需要连接电流传感器在A0引脚
*/
#define CURRENT_SENSOR_PIN A0
int findMinPwmByCurrent() {
Serial.println("基于电流检测自动寻找最小启动PWM...");
const int samples = 10;
int minStartPwm = -1;
float currentThreshold = 0.1; // 电流阈值,需要根据实际情况调整
// 先测量静止电流
float idleCurrent = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < samples; i++) {
idleCurrent += analogRead(CURRENT_SENSOR_PIN);
delay(10);
}
idleCurrent = idleCurrent / samples;
Serial.printf("电机静止电流: %.2f\n", idleCurrent);
// 扫描PWM值
for (int pwm = 0; pwm <= 200; pwm += 2) {
analogWrite(MOTOR_PWM_PIN, pwm);
digitalWrite(MOTOR_DIR_PIN, HIGH);
delay(500); // 等待稳定
// 测量当前电流
float current = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < samples; i++) {
current += analogRead(CURRENT_SENSOR_PIN);
delay(10);
}
current = current / samples;
float currentChange = abs(current - idleCurrent);
Serial.printf("PWM: %3d, 电流: %.2f, 变化: %.2f\n",
pwm, current, currentChange);
// 如果电流显著增加,说明电机开始转动
if (currentChange > currentThreshold && minStartPwm == -1) {
minStartPwm = pwm;
Serial.printf("🚀 检测到电机启动! PWM: %d\n", minStartPwm);
}
delay(200);
}
analogWrite(MOTOR_PWM_PIN, 0);
if (minStartPwm != -1) {
Serial.printf("✅ 自动检测最小启动PWM: %d\n", minStartPwm);
return minStartPwm;
} else {
Serial.println("❌ 未检测到电机启动,请检查连接");
return -1;
}
}
电流测量(基于ACS712)实例
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
// ACS712电流传感器示例
const int currentSensorPin = A0;
int sensorValue = 0;
int offsetValue = 512; // 零点偏移(无电流时输出,通常为Vcc/2)
float sensitivity = 0.185; // 灵敏度 (mV/A) - 根据型号调整
// 5A版本: 0.185V/A, 20A版本: 0.100V/A, 30A版本: 0.066V/A
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
Serial.println("ACS712电流传感器测试");
// 校准零点(确保无电流通过时测量)
calibrateZeroPoint();
}
void loop() {
float current = getCurrent();
Serial.print("电流: ");
Serial.print(current, 2);
Serial.println(" A");
delay(500);
}
void calibrateZeroPoint() {
Serial.println("校准中...确保无电流通过传感器");
delay(2000);
long sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
sum += analogRead(currentSensorPin);
delay(10);
}
offsetValue = sum / 100;
Serial.print("零点校准值: ");
Serial.println(offsetValue);
}
float getCurrent() {
int analogValue = 0;
// 多次采样取平均
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
analogValue += analogRead(currentSensorPin);
delay(1);
}
analogValue = analogValue / 10;
// 转换为电压 (Arduino ADC参考电压5V, 10位分辨率)
float voltage = (analogValue - offsetValue) * 5.0 / 1024.0;
// 转换为电流
float current = voltage / sensitivity;
return current;
}
4. 智能二分搜索法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
/**
* 使用二分法快速定位最小启动PWM
* 更高效的方法,适合精确确定
*/
int binarySearchMinPwm(int low, int high) {
Serial.println("使用二分法搜索最小启动PWM...");
Serial.println("请观察电机并在每次测试后输入反馈");
while (low <= high) {
int mid = (low + high) / 2;
Serial.printf("测试 PWM: %d - 电机是否转动? (y/n): ", mid);
analogWrite(MOTOR_PWM_PIN, mid);
digitalWrite(MOTOR_DIR_PIN, HIGH);
// 等待用户输入
while (!Serial.available()) {
delay(100);
}
char response = Serial.read();
analogWrite(MOTOR_PWM_PIN, 0); // 停止电机等待反馈
if (response == 'y' || response == 'Y') {
// 电机转动,尝试更小的值
high = mid - 1;
Serial.println(" ✓ 转动 -> 尝试更小值");
} else {
// 电机不转动,需要更大的值
low = mid + 1;
Serial.println(" ✗ 不转动 -> 尝试更大值");
}
delay(500);
}
int minPwm = low;
Serial.printf("✅ 最小启动PWM确定为: %d\n", minPwm);
return minPwm;
}
🎯 完整的多方法校准程序
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
#include <Arduino.h>
#define MOTOR_PWM_PIN D1
#define MOTOR_DIR_PIN D2
#define CURRENT_SENSOR_PIN A0
int minStartPwm = 80; // 默认值,将通过校准更新
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
pinMode(MOTOR_PWM_PIN, OUTPUT);
pinMode(MOTOR_DIR_PIN, OUTPUT);
pinMode(CURRENT_SENSOR_PIN, INPUT);
analogWriteRange(1023);
analogWriteFreq(1000);
Serial.println();
Serial.println("=== ESP8266 电机最小启动PWM校准系统 ===");
Serial.println("选择校准方法:");
Serial.println("1 - 手动交互校准");
Serial.println("2 - 自动步进扫描");
Serial.println("3 - 电流检测自动校准");
Serial.println("4 - 二分法快速定位");
Serial.println("c - 使用当前存储的最小PWM值");
Serial.printf("当前最小PWM: %d\n", minStartPwm);
}
void loop() {
if (Serial.available()) {
char method = Serial.read();
switch (method) {
case '1':
startManualCalibration();
break;
case '2':
autoScanMinPwm();
break;
case '3':
minStartPwm = findMinPwmByCurrent();
break;
case '4':
minStartPwm = binarySearchMinPwm(0, 200);
break;
case 'c':
Serial.printf("使用当前最小PWM: %d\n", minStartPwm);
testCurrentMinPwm();
break;
}
if (method >= '1' && method <= '4') {
Serial.println("校准完成!");
Serial.printf("最终确定的最小启动PWM: %d\n", minStartPwm);
Serial.println("选择其他方法或重新测试");
}
}
}
void startManualCalibration() {
Serial.println("手动校准模式 - 使用 '+' 和 '-' 调整PWM");
Serial.println("按 'y' 确认找到最小值,按 '0' 停止");
int pwm = 0;
bool calibrating = true;
while (calibrating) {
if (Serial.available()) {
char cmd = Serial.read();
switch (cmd) {
case '+': pwm = min(pwm + 5, 1023); break;
case '-': pwm = max(pwm - 5, 0); break;
case 'y':
minStartPwm = pwm;
calibrating = false;
break;
case '0':
pwm = 0;
calibrating = false;
break;
}
analogWrite(MOTOR_PWM_PIN, pwm);
digitalWrite(MOTOR_DIR_PIN, HIGH);
Serial.printf("当前PWM: %d\n", pwm);
}
delay(100);
}
analogWrite(MOTOR_PWM_PIN, 0);
}
void testCurrentMinPwm() {
Serial.printf("测试当前最小PWM值: %d\n", minStartPwm);
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
Serial.printf("测试 %d/3 - PWM: %d\n", i + 1, minStartPwm);
analogWrite(MOTOR_PWM_PIN, minStartPwm);
digitalWrite(MOTOR_DIR_PIN, HIGH);
delay(2000);
analogWrite(MOTOR_PWM_PIN, 0);
delay(1000);
}
Serial.println("测试完成,电机是否稳定启动?");
}
💡 专业校准技巧与建议
校准环境设置
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
/**
* 创建理想的校准环境
*/
void setupCalibrationEnvironment() {
Serial.println("设置校准环境...");
// 1. 设置较低的PWM频率以提高低速稳定性
analogWriteFreq(500);
// 2. 确保电机处于典型负载状态
Serial.println("请确保:");
Serial.println("- 电机连接实际工作负载");
Serial.println("- 电源电压稳定");
Serial.println("- 环境温度正常");
Serial.println("- 机械传动系统无卡涩");
delay(2000);
// 3. 预热电机(可选)
Serial.println("进行电机预热...");
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
analogWrite(MOTOR_PWM_PIN, 150);
delay(1000);
analogWrite(MOTOR_PWM_PIN, 0);
delay(500);
}
}
多重验证方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
/**
* 多重验证确定的最小PWM值
*/
bool validateMinPwm(int candidatePwm) {
Serial.printf("验证候选PWM值: %d\n", candidatePwm);
int successCount = 0;
const int totalTests = 5;
for (int i = 0; i < totalTests; i++) {
Serial.printf("验证测试 %d/%d: ", i + 1, totalTests);
analogWrite(MOTOR_PWM_PIN, candidatePwm);
digitalWrite(MOTOR_DIR_PIN, HIGH);
delay(2000);
// 这里可以添加实际的速度检测或电流检测
// 暂时使用用户反馈
Serial.println("电机是否稳定转动? (y/n)");
while (!Serial.available()) {
delay(100);
}
char response = Serial.read();
analogWrite(MOTOR_PWM_PIN, 0);
if (response == 'y' || response == 'Y') {
successCount++;
Serial.println(" ✓ 通过");
} else {
Serial.println(" ✗ 失败");
}
delay(1000);
}
float successRate = (float)successCount / totalTests * 100;
Serial.printf("验证成功率: %.1f%%\n", successRate);
return successRate >= 80.0; // 80%成功率认为有效
}
📋 校准结果记录与分析
数据记录结构
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
struct MotorCalibrationData {
int minStartPwm;
int voltage;
float temperature;
String loadCondition;
String timestamp;
float successRate;
};
void saveCalibrationData(int minPwm) {
MotorCalibrationData data;
data.minStartPwm = minPwm;
data.timestamp = String(millis());
data.successRate = 100.0; // 实际应该计算
Serial.println("=== 校准数据记录 ===");
Serial.printf("最小启动PWM: %d\n", data.minStartPwm);
Serial.printf("校准时间: %s\n", data.timestamp.c_str());
Serial.printf("成功率: %.1f%%\n", data.successRate);
Serial.println("====================");
}
🚀 使用建议
- 选择合适的校准方法:
- 初次校准:使用手动交互校准(方法1)
- 快速校准:使用二分法(方法4)
- 精确校准:使用电流检测(方法3)
- 考虑影响因素:
- 电源电压波动
- 环境温度变化
- 机械负载变化
- 电机磨损程度
- 定期重新校准:
- 建议在重要应用前进行校准
- 电机或负载更换后重新校准
- 环境条件显著变化时重新校准
通过这套完整的校准系统,你可以准确确定任何电机在ESP8266控制下的最小启动PWM值,为后续的精确速度控制奠定基础。